InventiAir has the most effective ACE
Air change effectiveness is a measurement of how effectively the air in a room is replaced. The University of Gävle has conducted a full-scale test with six workstations in a laboratory environment to measure precisely how well the air is ventilated. Effectiveness is determined using the quality assessment method for room ventilation, known as ACE..
ACE has been developed by the industry organisation ASHRAE and assesses air change effectiveness (ventilation index) at breathing height. In the test, InventiAir’s Cumulus Climate Device was compared with conventional mixing climate devices. Measuring points were set up at nine different points around the room, of which three were directly next to the workstations. On an ACE measurement, consideration is also given to the indoor climate. The result is an overall assessment of the ventilation’s effectiveness, energy consumption and environmental impact.
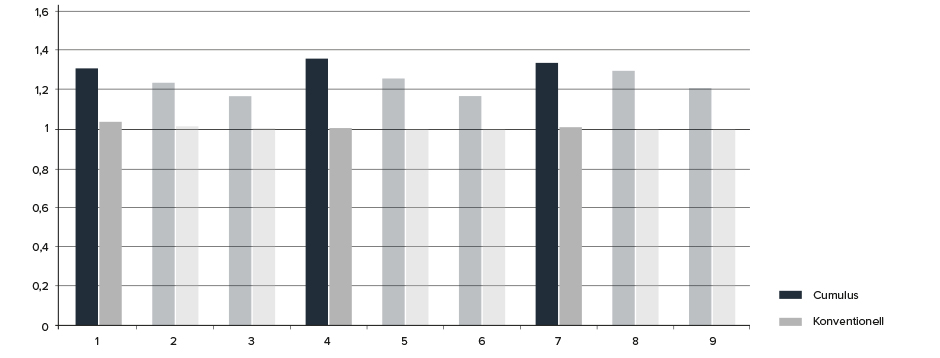
In the graph above, we can see that:
- The conventional cooling baffles are characterised by full mixing at all points (at the value 1.0)
- Cumulus is the most effective around the measuring points next to the workstations (1, 4 and 7)
- Cumulus is generally better performing, regardless of measuring point
The conclusion of the test is that InventiAir’s Cumulus can reduce the airflow by up to 25% without any loss in effectiveness. Reducing the airflow by 25% delivers energy savings in excess of 50% in the central fan. Quite simply, Cumulus has by far the most effective air change characteristics.
Read moreThe climate beam Cumulus – focusing on ventilating people
The University of Gävle and InventiAir will continue measuring air change in test environments for some time to come. The aim is to find a way of further enhancing the efficiency of the ventilation by focusing on CRE (Contaminant Removal Efficiency): how best to remove harmful particles, viruses and bacteria from a defined area by means of ventilation.
